Yogasana
Yoga an ancient but perfect science, deals with the evolution of humanity. It is integrated development of man: physical, mental and emotional. is a discipline that enables man to actualize his potential to the fullest extent through self-culture and self-education. It expounds certain techniques and methods that would enable man to have union with the self(the Divine).The constant practice of yoga helps in developing the virtues of humanity and peace of mind, which ultimately enable man to have a peaceful and cordial relationships with others.
Yogic Asanas are meant to tone up the internal organs of the body and to revitalize the working of the endocrine glands. On the other hand, physical exercise are meant to built muscles of the body. Yogic Asanas ensure better health, where as physical exercises provide good physique. However, Yogic Asanas and physical exercise can be practiced simultaneously.
Modern-day science confirms that the practice of yoga has tangible physical health benefits that include improve brain function and denser bones, as well as immune health, improved nervous system functioning and strength.
Yogasans are techniques to bring about very deepest to different parts of body. This is achieved by performing the postures.

Utrasana
Ustrasana is a deep backward bend from a kneeling position; the completed pose has the hands on the heels. The backs of the feet may be flat on the floor, or the toes may be tucked under for a slightly less strong backbend. The pose is one of the 26 asanas in the Bikram Yoga sequence.
Benefits
- Reduces fat on thighs.
- Opens up the hips, stretching deep hip flexors.
- Stretches and strengthens the shoulders and back.
- Expands the abdominal region, improving digestion and elimination.
- Improves posture.
- Opens the chest, improving respiration.
- Loosens up the vertebrae.

Vrikshasana
Tree Pose or Vrikshasana is a basic balancing pose that we all need in our practice. It replicates the graceful, steady stance of a tree. This pose is a form of standing meditation which is something we all could use to clear our minds of useless negative thoughts. Unlike most yoga poses, the Tree Pose requires keeping our eyes open in order to maintain body balance. Vrksasana clarifies just how challenging it can be to stand on one leg.
Benefits
- Improves balance and stability in the legs.
- On a metaphysical level, helps one to achieve balance in other aspects of life.
- Strengthens the ligaments and tendon of the feet.
- Strengthens and tones the entire standing leg, up to the buttocks.
- Assists the body in establishing pelvic stability.

Natarajasana
Natarajasana or Lord of the Dance Pose is an asana. Sanskrit: नटराजासन; Nata- Dance, Raja- King, Asana – Pose; Pronounced As – nut-ah-raj-AHS-anna Nataraja is one of the many names of Lord Shiva. It is his dancing avatar, through which his love for music, dance, and art is depicted. If this asana is done properly, it resembles one of the dancing poses of Lord Shiva. Take a look at everything this asana has to offer.
Benefits
- Practicing this asana gives strength to your chest, ankles, hips, and legs.
- This asana increases your metabolism and helps in weight loss.
- It gives your groin, abdominal organs, and thighs a good stretch.
- Your posture is improved, and balance is increased.
- It helps better your digestion.

Parsakonasana
Parsvakonasana (Sanskrit: उत्थित पार्श्वकोणासन, utthita pārśvakoṇāsana), Extended Side Angle Pose, is an asana in modern yoga as exercise. It involves using many essential muscle groups: legs, ankles, groin, chest, lungs, shoulders, spine, and the abdomen.
Benefits
- Strengthens and stretches the legs, knees, and ankles.
- Stretches the groins, spine, waist, chest and lungs, and shoulders.
- Stimulates abdominal organs.
- Increases stamina.

Vajrasana
Vajrasana is the Sanskrit name for a seated yoga asana. This posture provides a deep stretch for the quadriceps and the tops of the feet, and is believed to assist in digestion. Vajrasana can be used as a transitional or resting pose between other asana, and it is often used as a posture for meditation.
Benefits
- Aiding in digestion.
- Relieving or preventing constipation.
- Strengthening pelvic muscles.

Sarvangasana
The word Sarvangasana had been taken from Sanskrit सर्वाङ्गासन. It is consisted of three words Sarv, Anga and Asana. The meaning of sarva is Entire; anga is Parts of the body and asana means yogic posture. In English, it is known as Shoulder stand yoga pose.
Benefits
- Calms the brain and helps relieve stress and mild depression.
- Stimulates the thyroid and prostate glands and abdominal organs.
- Stretches the shoulders and neck.
- Tones the legs and buttocks.
- Improves digestion. Helps relieve the symptoms of menopause.
- Reduces fatigue and alleviates insomnia.

Sirshasana
Image result for Sirsasana description Salamba Shirshasana, often shortened to Shirshasana, or Yoga Headstand is an inverted asana in modern yoga as exercise; it was described as both an asana and a mudra in classical hatha yoga, under different names.
Benefits
- Calms the brain and helps relieve stress and mild depression.
- Stimulates the pituitary and pineal glands.
- Strengthens the arms, legs, and spine.
- Strengthens the lungs.
- Tones the abdominal organs.
- Improves digestion.
- Helps relieve the symptoms of menopause.
- Therapeutic for asthma, infertility, insomnia, and sinusitis.

Sashankasana
The word Shashankasana has been derived from Sanskrit word shashank means ‘moon’. Hence, it is named as Moon pose. On the other hand, shash means hare and ank means lap, therefore, it is called as Hare pose or Rabbit pose. Shashankasana imitates Hare pose or Rabbit pose in the final stage, hence named as hare.
Benefits
- Blood circulation keeps the body youthful and energetic.
- Fatigue is kept at bay and head related ailments subside.
- Depression or mental disorders take a backseat.
- Aids in concentration and focus.
- Strengthens hamstrings, back and hip flexors.
- Complete relaxation for the anterior muscles.
- Digestive Muscles get a good massage because of abdominal breathing

Padmasana
Lotus position or Padmasana is a cross-legged sitting meditation pose from ancient India, in which each foot is placed on the opposite thigh. The pose can be uncomfortable for people not used to sitting on the floor, and attempts to force the legs into position can injure the knees.
Benefits
- Opens up the hips.
- Stretches the ankles and knees.
- Calms the brain.
- Increases awareness and attentiveness.
- Keeps the spine straight.
- Helps develop good posture.
- Eases menstrual discomfort and sciatica.
- Helps keeps joints and ligaments flexible.

Bhujangasana
Bhujangasana or Cobra Pose is a reclining back-bending asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. It is commonly performed in a cycle of asanas in Surya Namaskar (Salute to the Sun) as an alternative to Urdhva Mukha Svanasana (Upwards Dog Pose).
Benefits
- Strengthens the spine.
- Stretches chest and lungs, shoulders, and abdomen.
- Tones the buttocks. Stimulates abdominal organs. Helps relieve stress and fatigue.
- Opens the heart and lungs.
- Soothes sciatica. Therapeutic for asthma.

Dhanurasana
Dhanurasana is an intermediate level back bending yoga posture. Akarshana Dhanurasana is a yoga position that resembles to a bow stretched with an arrow ready to be shot. It is a sitting yoga position where the big toes are held by the hands and one of them is stretched towards the ear.
Benefits
- Stretches the entire front of the body, ankles, thighs and groins, abdomen and chest, and throat, and deep hip flexors (psoas).
- Strengthens the back muscles.
- Improves posture.
- Stimulates the organs of the abdomen and neck.

Halasana
Halasana or Plough pose, is an inverted asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Its variations include Karnapidasana with the knees by the ears, and Supta Konasana with the feet wide apart.
Benefits
- Calms the brain.
- Mitigates the effect of a backache.
- Betters digestive process.
- Strengthens the abdomen muscles.
- Good for arms and shoulders.
- Promotes blood circulation.
- Improves body balance.
- Therapeutic for a headache.
- Stretches the thighs muscles.
- Refines body flexibility.

Ardha Matsyendrasana
Ardha Matsyendrasana (Half Lord of the Fishes Pose) is named after the great yogi Matsyendranath who founded Hatha Yoga. The English name, Half Lord of the Fishes Pose, comes from the Sanskrit words ‘ardha’ = ‘half’, ‘matsya’ = ‘fish’, ‘eendra’ = ‘king’. This yoga pose has other variations and can be referred as Half Spinal Twist Pose or Vakrasana (which means twist).
Benefits
- It strengthens and tones your obliques and abs.
- The pose energizes and stretches the spine.
- Open your shoulders, hips and neck.
- Increase the flexibility in your spine and hips.

Trikonasana
Trikonasana or Utthita Trikonasana, [Extended] Triangle Pose is a standing asana in modern yoga as exercise. Variations include Baddha Trikonasana (bound triangle pose) and Parivrtta Trikonasana (revolved triangle pose).
Benefits
- It helps our body to relieves gastritis, indigestion, acidity and flatulence.
- The triangle pose done by bending your body to either sides simultaneously, improves the flexibility of the spine and alleviates backache to a very extend.

Salabasana
Salabhasana, Shalabhasana, Locust pose, or Grasshopper pose is a reclining back-bending asana in modern yoga as exercise.
Benefits
- Strengthens the muscles of the spine, buttocks, and backs of the arms and legs.
- Stretches the shoulders, chest, belly, and thighs. Improves posture.
- Stimulates abdominal organs.
- Helps relieve stress.
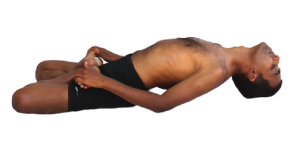
Matyasana
Matsyasana or Fish pose is a reclining back-bending asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. It is commonly considered a counterasana to Sarvangasana, or shoulder stand, specifically within the context of the Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga Primary Series.
Benefits
- Better Spinal Health
- Beneficial for Thyroid
- Toned Glutes
- Lightens Mood
- Beat the Stress
- Healing from Within
- Weight Loss

Padahasthasana
Padahastasana is a stretch pose that uses the strength of the body to stretch. Padahastasana is derived from the Sanskrit names pada which means foot, hasta which means hand and asana meaning pose. Padahastasana, therefore, translates to hand to feet pose in English.
Benefits
- Massages the digestive organs.
- Alleviates flatulence, constipation and indigestion.
- Spinal nerves are stimulated and toned.
- Increases vitality.
- Improves the metabolism.
- Improves concentration.
- Helps with nasal and throat disases.

Tadasana
Tadasana (Sanskrit: ताडासन; IAST: Tāḍāsana), Mountain Pose or Samasthiti (Sanskrit: समस्थिति; IAST: samasthitiḥ) is a standing asana in modern yoga as exercise; it is not described in medieval hatha yoga texts. It is the basis for several other standing asanas.
Benefits
- The biggest benefit of tadasana is that it helps in correcting your posture and improves your balance by making your spine more agile.
- It helps in increasing the flexibility of your ankles, thighs and joints.
- It can tone your hips and abdomen and helps to gain control over your muscular movements.

Anjaneyasana
Āñjaneyāsana (Sanskrit: आञ्जनेयासन, “Son of Anjani pose”), Crescent Moon Pose or Ashwa Sanchalanasana, Equestrian Pose is a lunging back bending asana in modern yoga as exercise. It is sometimes included as one of the asanas in the Surya Namaskar sequence, though usually with arms down in that case.
Benefits
- Activates the Functioning of Thyroid Glands
- A Heart Opening Yoga Posture.
- Flexible Lower Body.
- Therapeutic for Sciatica.
- Beneficial for Abdomen.
- A Gentle Backbend
- An Alternative to Warrior I
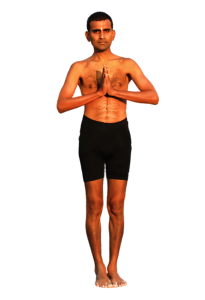
Pranamasana
Pranamasana or the Prayer Pose is the starting pose for Surya Namaskara or the Sun Salutation poses. In Pranamasana, the palms are held together in the prayer pose. The word ‘Pranam’ has a Sanskrit root and it means ‘to pay respect’; and asana means a pose. Hence the name Pranamasana.
Benefits & Limitations
- Relaxes the Mind and Soul.
- Brings Awareness.
- Enhances Body Posture.
- Body-Mind Balance.
- Instils Spiritual Energy to the Mind.

Garudasana
Garudasana is an asymmetric position in which one leg, say the right, is crossed over the left, while the arm on the opposite side, say the left, is crossed over the right, and the palms are pressed together. Like all poses on one leg, it demands, and may help to build, balance and concentration.
Benefits & Limitations
- Strengthens and stretches the ankles and calves.
- Stretches the thighs, hips, shoulders, and upper back.
- Improves concentration. Improves sense of balance.
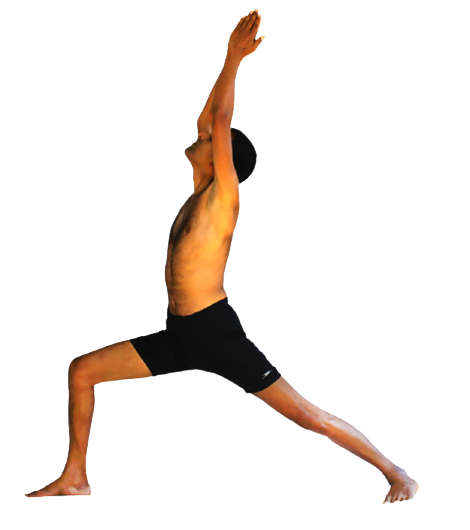

Veerabhadrasana ( Variation1)
Virabhadrasana Warrior Pose is a group of related lunging standing asanas in modern yoga as exercise commemorating the exploits of a mythical warrior, Virabhadra.
Benefits & Limitations
- In this pose chest is fully expanded and this helps in deep breathing.
- Relieves stiffness in neck, shoulders and back, benefits ankles and knees.
- It is good for gastric trouble and acidity.
- High blood pressure and vertigo.
- Should not stay long in this asana.

Veerabhadrasana ( Variation2)
Virabhadrasana Warrior Pose is a group of related lunging standing asanas in modern yoga as exercise commemorating the exploits of a mythical warrior, Virabhadra.
Benefits & Limitations
- Strengthens and stretches leg muscles, ankles, chest, lungs and shoulders.
- Therapeutic for carpel tunnel syndrome, flat foot, infertility, osteoporosis and sciatica.
- Those with knee problems should not bend to 90 degrees.

Paschimottanasana
Paschimottanasana Seated Forward Bend or Intense Dorsal Stretch is a seated forward-bending asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise.
Benefits & Limitations
- Calms the brain and helps relieve stress and mild depression.
- It is good for gastric trouble and acidity.
- Stimulates the liver, kidneys, ovaries, and uterus.
- Improves digestion. Helps relieve the symptoms of menopause and menstrual discomfort.
